Understanding the Foundation of Data Pipelines
In today’s data-driven business landscape, organizations generate and consume vast amounts of information every second. From customer interactions and sales transactions to operational metrics and market intelligence, data flows continuously through various touchpoints. However, raw data in its unprocessed form provides little value to decision-makers. This is where data pipelines become absolutely crucial for modern businesses.
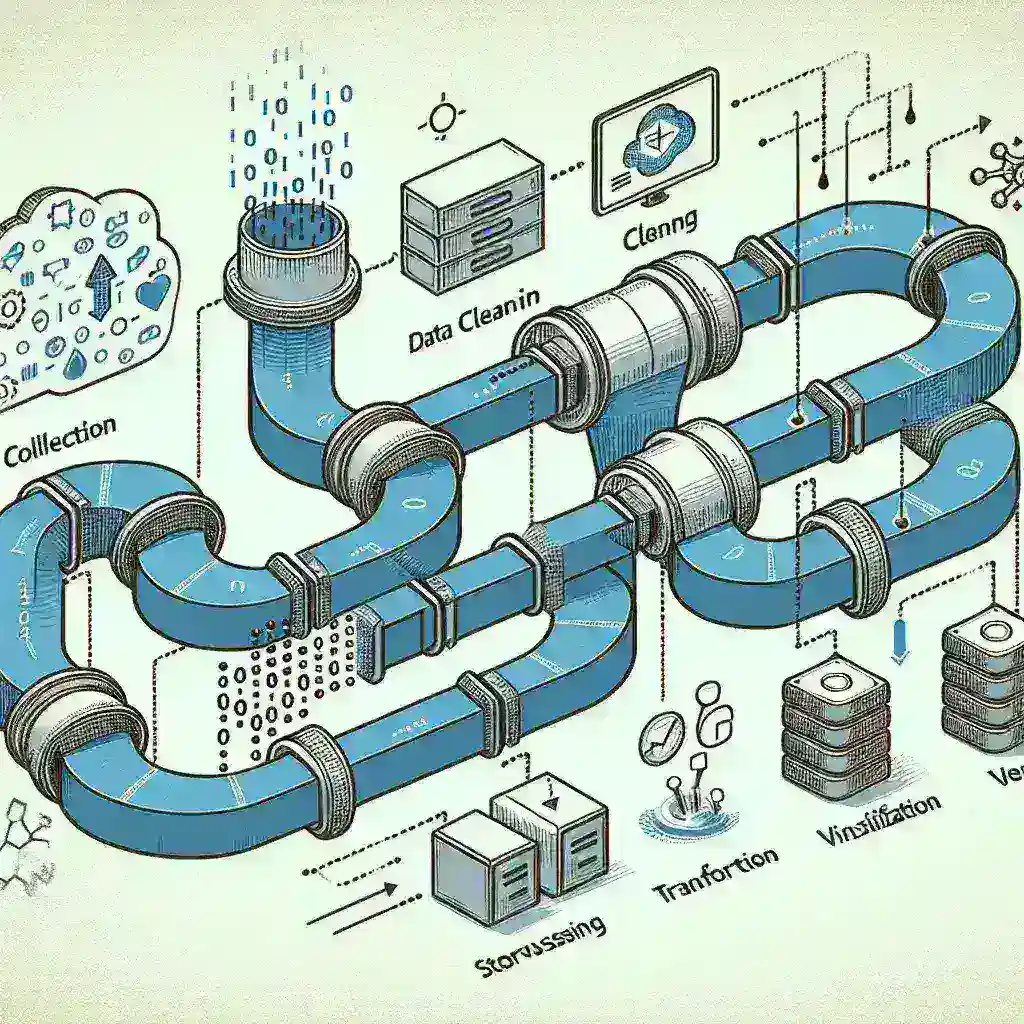
A data pipeline represents the systematic process of moving data from multiple sources, transforming it into a usable format, and delivering it to designated destinations where it can drive meaningful insights. Think of it as a sophisticated highway system that ensures data travels efficiently from point A to point B while maintaining quality, security, and reliability throughout the journey.
Core Components of a Robust Data Pipeline Architecture
Building an effective data pipeline requires understanding its fundamental components and how they work together to create a seamless data flow. Each element plays a critical role in ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
Data Ingestion Layer
The ingestion layer serves as the entry point where data from various sources enters your pipeline. This component must handle different data formats, frequencies, and volumes while maintaining consistency. Batch processing works well for large volumes of historical data that don’t require real-time processing, while stream processing handles continuous data flows that need immediate attention.
Modern businesses typically deal with diverse data sources including databases, APIs, file systems, IoT devices, and third-party applications. Your ingestion layer should accommodate this variety while providing reliable connectivity and error handling mechanisms.
Data Transformation Engine
Raw data rarely comes in the perfect format for analysis. The transformation engine applies business rules, cleans inconsistencies, standardizes formats, and enriches data with additional context. This stage often involves complex operations like data validation, deduplication, aggregation, and schema mapping.
Effective transformation processes ensure data quality while maintaining performance. Consider implementing data lineage tracking to understand how data changes throughout the transformation process, enabling better debugging and compliance reporting.
Storage and Processing Infrastructure
Your storage strategy should balance performance, cost, and scalability requirements. Data lakes provide flexibility for storing various data types in their native formats, while data warehouses offer structured environments optimized for analytical queries. Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach, leveraging both technologies based on specific use cases.
Cloud-based solutions have revolutionized data storage by offering virtually unlimited scalability and pay-as-you-use pricing models. Major providers like Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure offer comprehensive data services that can significantly reduce infrastructure complexity.
Strategic Planning for Pipeline Implementation
Successful data pipeline implementation requires careful planning and consideration of business requirements, technical constraints, and future growth projections.
Assessing Business Requirements
Begin by conducting a thorough analysis of your organization’s data needs. Identify key stakeholders, understand their data consumption patterns, and define success metrics. Consider questions like: What types of insights do different departments need? How frequently should data be updated? What are the acceptable latency requirements?
Document your current data sources and their characteristics, including volume, velocity, variety, and veracity. This assessment will guide technology selection and architecture decisions throughout the implementation process.
Choosing the Right Technology Stack
Technology selection should align with your business requirements, team expertise, and budget constraints. Open-source solutions like Apache Kafka, Apache Spark, and Apache Airflow offer powerful capabilities with lower licensing costs but require more technical expertise. Commercial platforms provide user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive support but may involve higher expenses.
Consider factors such as scalability, integration capabilities, learning curve, community support, and long-term viability when evaluating different options. The goal is to build a sustainable solution that can evolve with your business needs.
Implementation Best Practices and Methodologies
Building reliable data pipelines requires adherence to proven best practices that ensure quality, performance, and maintainability.
Designing for Reliability and Fault Tolerance
Implement comprehensive error handling mechanisms that can gracefully manage various failure scenarios. Design your pipeline with redundancy and failover capabilities to minimize downtime impact. Use techniques like circuit breakers, retry logic with exponential backoff, and dead letter queues to handle transient failures effectively.
Monitoring and alerting systems should provide real-time visibility into pipeline health and performance. Set up alerts for critical metrics like data volume anomalies, processing delays, and error rates to enable proactive issue resolution.
Ensuring Data Quality and Governance
Implement data quality checks at multiple stages of your pipeline to catch issues early. Define clear data quality rules and validation criteria based on business requirements. Consider implementing data profiling tools that can automatically detect anomalies and quality issues.
Establish data governance policies that define data ownership, access controls, retention policies, and compliance requirements. Document data definitions, business rules, and transformation logic to ensure consistency and facilitate troubleshooting.
Optimizing Performance and Scalability
Design your pipeline architecture to handle current data volumes while accommodating future growth. Implement partitioning strategies that enable parallel processing and improve query performance. Use caching mechanisms strategically to reduce processing overhead for frequently accessed data.
Regular performance testing and optimization should be part of your maintenance routine. Monitor resource utilization patterns and adjust infrastructure capacity based on actual usage trends.
Security Considerations and Compliance
Data security must be integrated into every aspect of your pipeline design, not treated as an afterthought. Implement encryption for data in transit and at rest, using industry-standard protocols and key management practices.
Access controls should follow the principle of least privilege, ensuring users and applications only have access to the data they need for their specific functions. Implement audit logging to track data access and modifications for compliance and security monitoring purposes.
Consider regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards that may apply to your organization. Design your pipeline to support data privacy requirements like data anonymization, right to be forgotten, and consent management.
Testing and Validation Strategies
Comprehensive testing ensures your pipeline performs reliably under various conditions. Implement unit tests for individual components, integration tests for end-to-end workflows, and performance tests for scalability validation.
Create test datasets that represent realistic scenarios, including edge cases and error conditions. Automate testing processes as part of your continuous integration and deployment pipeline to catch issues early in the development cycle.
Validate data accuracy by comparing pipeline outputs with expected results using statistical methods and business logic verification. Implement data reconciliation processes that can detect discrepancies between source systems and pipeline outputs.
Monitoring, Maintenance, and Continuous Improvement
Establishing robust monitoring and maintenance practices ensures long-term pipeline reliability and performance. Implement comprehensive logging that captures detailed information about data processing activities, system performance, and error conditions.
Create operational runbooks that document common troubleshooting procedures, escalation processes, and recovery steps. Train your team on pipeline operations and ensure knowledge transfer to prevent single points of failure.
Regular pipeline health assessments should evaluate performance trends, identify optimization opportunities, and plan for capacity upgrades. Collect feedback from data consumers to understand their evolving needs and adjust pipeline capabilities accordingly.
Future-Proofing Your Data Pipeline Investment
Technology landscapes evolve rapidly, and your data pipeline should be designed to adapt to changing requirements and emerging technologies. Adopt modular architectures that allow component replacement without major system overhauls.
Stay informed about industry trends like real-time analytics, machine learning integration, and edge computing that may impact your data strategy. Plan for emerging data sources and formats that your organization may need to incorporate in the future.
Consider implementing DataOps practices that bring software development methodologies to data pipeline management. This approach emphasizes collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement to enhance pipeline reliability and agility.
Building a reliable data pipeline requires careful planning, appropriate technology selection, and adherence to best practices throughout the implementation process. By focusing on reliability, scalability, and security from the outset, organizations can create data infrastructure that supports informed decision-making and drives business growth. Remember that pipeline development is an iterative process that benefits from continuous monitoring, optimization, and adaptation to changing business needs.

Leave a Reply